Polyvinyl Alcohol vs Polyvinyl Acetate--Shocking Differences
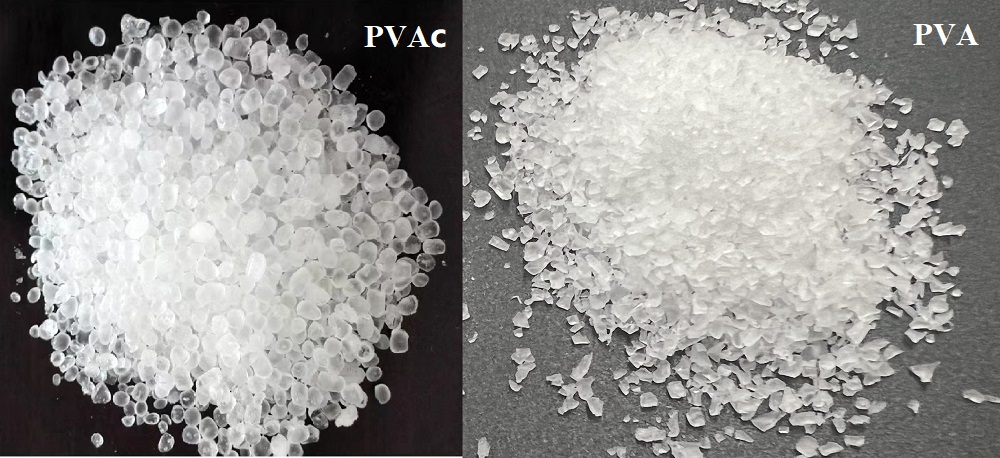

Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) and Polyvinyl Acetate (PVAc) are two types of vinyl polymers with distinct properties and applications. While they share some similarities, such as being water-soluble and used in the production of adhesives and coatings, there are also significant differences between the two. In this article, we will compare PVA and PVAc in terms of their properties and applications.
polyvinyl alcohol vs polyvinyl acetate Uses Comparison
Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)
PVA is a water-soluble synthetic polymer that is produced by the hydrolysis of polyvinyl acetate. This process involves the replacement of acetate groups with hydroxyl groups, resulting in a polymer that is highly soluble in water. PVA application including:
Packaging: PVA is commonly used as a water-soluble packaging material for detergents, agricultural chemicals, and other products.
Textiles: PVA fibers are used in the production of textiles, particularly in the manufacture of artificial silk.
Adhesives: PVA is used as a binder in the production of adhesives, particularly in the woodworking industry.
Coatings: PVA is used as a coating material to provide a smooth surface on paper and textiles.
One of the main advantages of PVA is its biodegradability, which makes it an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic polymers. However, PVA is also sensitive to moisture, which can cause it to lose its adhesive properties.
Polyvinyl Acetate (PVAc)
PVAc was first discovered by the German scientist “Dr. Fritz Klatte” in 1912. PVAc is formed by polymerization of vinyl acetate in the presence of acetic acid. Polyvinyl acetate uses including:
Adhesives: PVAc is widely used in the production of polyvinyl acetate adhesive for woodworking and other applications.
Coatings: PVAc is used as a coating material to provide a smooth surface on paper and textiles.
Packaging: PVAc is used as a coating material for paper and cardboard packaging to improve its water resistance.
Gum base: PVAc is used as a base for chewing gum to improve its texture and shelf life.
PVAc is the raw material of PVA, which is one of the main uses of PVAc.
One of the key advantages of PVAc is its high adhesion strength, which makes it ideal for use in adhesive applications. However, PVAc is also sensitive to heat, which can limit its use in high-temperature applications.


polyvinyl alcohol vs polyvinyl acetate Properties Comparison
While PVA and PVAc share some similarities, such as being water-soluble and used in the production of adhesives and coatings, there are also significant differences between the two. Here’s a summary of their key differences:
Solubility: PVA is highly soluble in water, while PVAc is less soluble.
Adhesion strength: PVAc has higher adhesion strength than PVA.
Heat resistance: PVAc has higher heat resistance than PVA.
In conclusion, PVA and PVAc are two distinct vinyl polymers with different properties and applications. While they share some similarities, their differences make them better suited for specific applications. Understanding the differences between PVA and PVAc can help you choose the right material for your specific needs.